Author : Ashley Mehta
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality in Healthcare
Top Five Areas
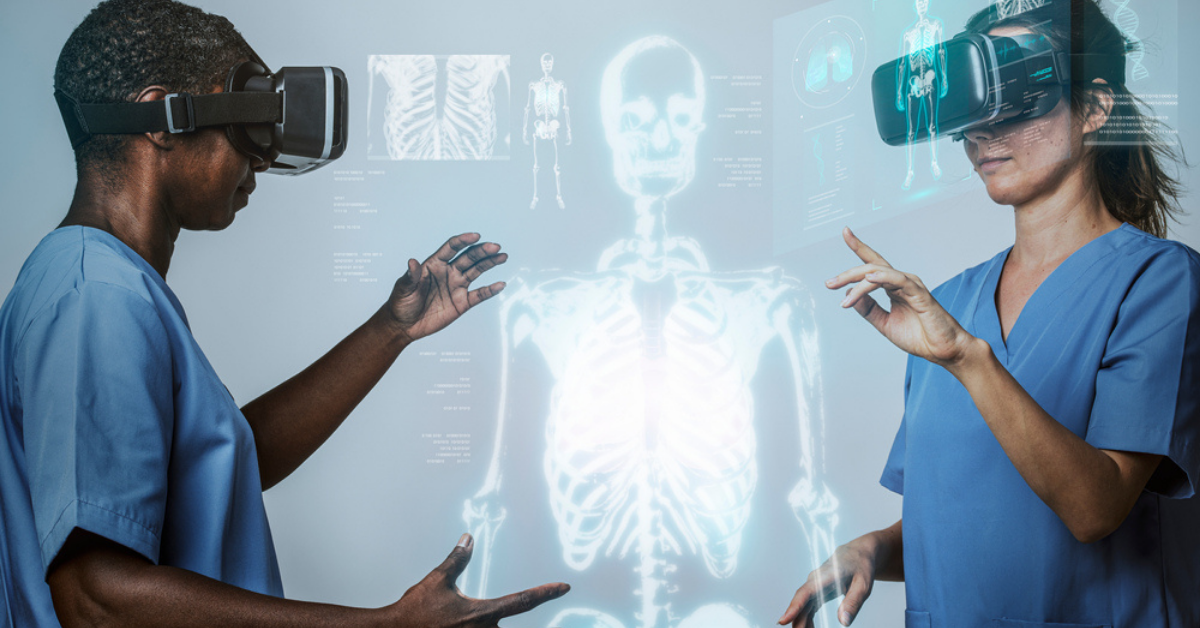
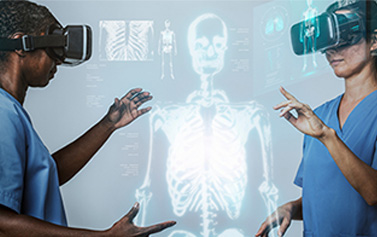
Immersive technologies such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR) and 3D software are changing our lives and disrupting diverse industries across the globe. AR/VR technologies are being used in business, education, gaming and healthcare. In the medical industry, virtual training and procedures are becoming the gold standard, especially in surgery. Companies like Intuitive Surgical, famous for its robotic-assisted surgery system (the Da Vinci system), are now moving into virtual reality. Surgeons are currently using tools that range from VR headsets to haptic gloves to mimic real-life surgical procedures, boosting preparedness and efficiency in the operating room. With VR and AR, surgeons now have pre-surgery access to 3D images of hearts, eyes, knee joints and more.
VR has a multitude of benefits for surgeons, medical professionals, patients —here are the top five areas.
1. Surgical Assistance
AR and VR help surgeons plan their procedures in advance and better visualize complicated surgeries. 3D models provide a better understanding of the anatomy and spatial relationships of organs that help surgeons to better prepare for complex procedures where they need to access hard-to-reach areas. This improves patient outcomes as well as reduces risks during surgery because they are better prepared for what they will face.
VR provides them with an immersive experience that surgeons would not get otherwise, which can result in more accurate diagnoses and less mistakes. AR and VR technologies can be used in all surgical fields, but they are mostly used in cardiothoracic surgery, orthopedic surgery, neurosurgery and ophthalmology.
2. Virtual Training
The implementation of VR and AR solutions can considerably simplify the entire process of medical school education and subsequent training. Advances in AR/VR allow detailed study of the human anatomy layer by layer, along with the mechanics of the human body, in an interactive environment. This gives surgical fellows profound insight into nuances of different body functions.
Cutting-edge technology is especially important when it comes to surgical training as it is almost impossible to imitate near-real life conditions to prepare professionals. VR training enables medical professionals to practice and upgrade their skills without having to be physically present at a hospital. With VR equipment like headsets and sensors, medical scenarios can be recreated, enabling the trainee to experience them actively instead of just as a passive spectator.
3. Remote Guidance
AR/VR is increasingly being used in the medical field to provide remote assistance to doctors performing surgery. A remote assistance solution based on AR/VR, such as an app, enables physicians to collaborate during surgeries or have an effective virtual meeting on medical issues. A two-way video and audio headset allows both professionals to see the same view of the patient. This way, a remote specialist can guide a surgeon during real-time surgery. Thus, the patient can get better treatment and a safer outcome.
It has been proven that AR/VR can provide better results than using video chat, which has been the traditional method of providing remote assistance. Doctors can also observe rehabilitation patients more effectively using the remote assistance solution and provide superior treatment.
4. Advanced Diagnostics
Diagnosis is a critical part of healthcare and relies heavily on precise results, accurate details and a close assessment of symptoms. AR and VR can be effectively employed to detect, help treat and even prevent various diseases more efficiently. VR visualizes information coming from multiple sensors into a single cohesive interface and shows potential causes of a patient’s condition via analysis. Using AR and VR, healthcare providers can more easily gather details, statistics and reports pertaining to a patient.
AR-enabled tools, like full-body scans and thermal imaging, allow medical practitioners to perform a complete internal examination of the patient, such as checking organs, veins, muscles and bones, without performing invasive procedures and leading to a precise diagnosis.
Lastly, diagnoses with AR and VR technology eliminate the need for personal PPE (protection equipment) by minimizing contact between the patient, nurse, doctor, and other medical support personnel.
5. Telehealth
AR in telehealth or remote medical care is on the rise. The pandemic has propelled telehealth to the top as the preferred way for receiving and providing healthcare as it reduces the risk of contracting Covid-19. There are long-term implications for the healthcare sector of using AR/VR in telemedicine.
AR/VR technologies are being increasingly used to deliver remote patient care, telemedicine, and assistive care for patients who are homebound or confined to hospital beds. Patients are able to interact with their doctors in a more personal way and have a conversation with them in real time. It is a boon for patients with chronic illnesses who cannot travel far away from home to see specialists in person.
Additionally, AR or VR supported telemedicine is poised to play a major role in post-pandemic strategies for managing infectious disease outbreaks. They have helped in reducing exposure to viruses for both doctors and patients, without compromising on the quality of care.
Thus, it is evident that due to their wide-ranging applications, AR and VR are rapidly gaining momentum. It makes business sense that the healthcare sector will invest in it to achieve greater efficiency.